2017-2018
Self-driving explorer robot
The goal of the project was to create a self-driving robot that can be controlled remotely or, if the self-guiding mode is activated, can drive around the space available without external commands, or help, and collect data from it.
A few pictures of the prototype:
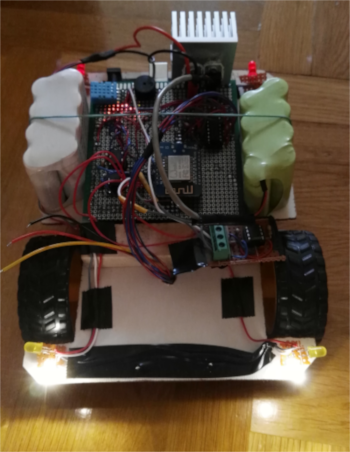

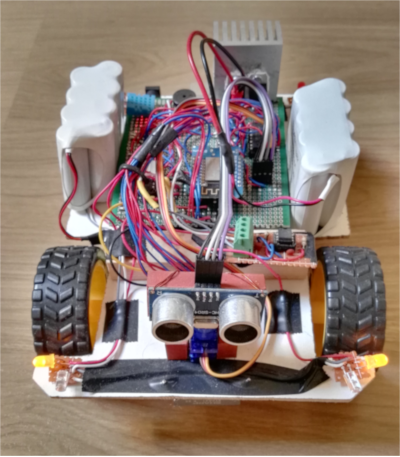
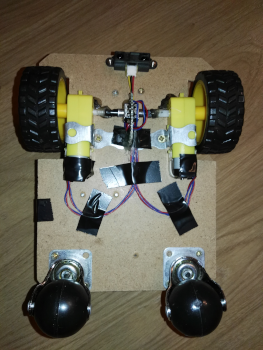
The project's details:
Two microcontrollers are responsible for controlling the prototype. An Arduino Mega controls the movements, it calculates the best ways to avoid objects while driving, and it reads the data coming from the different sensors. The wireless communication and the real-time data transfer is done by an ESP8266 module. It transfers the data of every sensor of the device to a server, and the users can read the data processed by the server. These contain relative humidity level, temperature, the robot's GPS coordinates, the current distance between the robot and the nearest object (with the help of a turnable ultrasound sensor), and some information about the air quality near the robot (with the help of an MG-135 sensor). From this data, a 2dimension map can be generated, from the free places of the given room. The robot can detect the edge of an object under it, with an infrared sensor, and can avoid falling from the top of a box, or a table. The map can be generated in various ways. For example, we can use the ultrasound sensor's data and the GPS coordinates (the GPS coordinates can be more precise using the rotation encoders connected to the wheels), and using this method we will get a map of the areas accessible by the robot. But we can use every sensor at the same time, and taking the external temperature, the air quality ...etc. we can get a map of the "safe zones" where the measured values are safe for humans and animals. This function can be useful, for example, at the site of a natural disaster.